What Are the Symptoms of PTSD?
Jul 08, 2021PTSD is usually diagnosed after a person experiences ongoing symptoms for at least a month following a traumatic event. Nevertheless, symptoms may not appear until several months or even years later. PTSD is represented by three main types of symptoms:
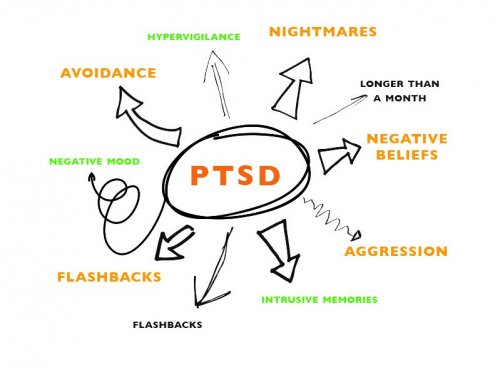
- Re-experiencing the trauma through intrusive disturbing recollections of the event, flashbacks, & nightmares.
- Emotional impassivity & avoidance of places, people, and activities that are reminders of the trauma.
- Increased arousal such as difficulty sleeping & concentrating, feeling jumpy, and being easily irritated & angered.
To be diagnosed with PTSD, an adult must have all of the following for at least 1 month:
At least one re-experiencing symptom: Flashbacks, distressing thoughts, physical signs, reoccurring memories or dreams related to the event
At least one avoidance symptom: Staying away from places, events, or objects that are reminders of the experience, or avoiding thoughts or feelings related to the traumatic event
At least two arousal & reactivity symptoms: being easily startled, feeling tense or on edge, having difficulty concentrating, having trouble falling asleep or staying asleep, feeling irritable and having angry or aggressive outbursts, and engaging in risky, reckless, or destructive behavior.
At least two cognition and mood symptoms: loss of interest in previous activities that were enjoyable, trouble remembering key points of the traumatic event, negative thoughts about the event leading to blame, negative thoughts about oneself or the world, feelings of social isolation, and ongoing negative emotions like fear, anger, guilt, or shame.

